food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome wiki
FPIES presents in infants with repetitive continued vomiting that begin approximately 1-4 hours after the allergenic food is eaten. Purpose of review.

Elecare Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome
Acute FPIES reactions generally occur in children ages 412 months 14 hours after ingestion of the trigger food.

. By using our services you agree to our use of cookies. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe non IgE delayed form of food allergy. Typical symptoms of FPIES include severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration two hours after eating.
Recent Findings FPIES affects. Food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome wiki Sunday May 29 2022 Edit The acute form of hepatitis generally caused by viral infection is characterized by constitutional symptoms that are typically self-limiting. Since the advent of a specific diagnostic code and establishment of diagnostic guidelines our understanding of this condition has grown.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a severe systemic response to food protein that typically occurs 1 to 4 hours after the ingestion of the causative food and frequently develops in the first few years of lifeIn the severe form patients will vomit until dehydration and until a shock-like state which occurs in 15 of patients. Cookies help us deliver our services. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to weight loss failure to.
Purpose of Review Food proteininduced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy characterized by delayed and potentially severe gastrointestinal symptoms. The most common FPIES food triggers are cows milk soy rice and oats but any food can cause FPIES symptoms. Acute food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated allergy and is characterized by repetitive profuse vomiting episodes often in association with pallor lethargy and diarrhea presenting within 14 h from the ingestion of a triggering food.
Cows milk soy grains egg and fish are among the. To increase understanding of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES a non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated reaction to food by reviewing a growing body of literature including recently published international consensus guidelines. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobin E IgE-mediated food hypersensitivity disorder that primarily affects formula-fed infants and young children 12The clinical manifestation of FPIES is characterized by profuse and repetitive vomiting usually occurring within a few hours of feeding accompanied by.
Diarrhea may occur within 24. The child may appear tired and ill with pale skin. The primary symptom is profuse repetitive vomiting.
These symptoms can lead to other complications including changes in blood pressure and body temperature lethargy and failure to. FPIES primarily affects infants and young children and is. It is much less common than IgE-mediated food allergy and typically occurs in babies and infants.

Yes Oats Can Cause Gas Here S Why Vojo

8 Common Food Allergies Causes Symptoms And Treatment

Fpies In A Mother S Eye Neocate

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Allergic Proctocolitis Abstract Europe Pmc
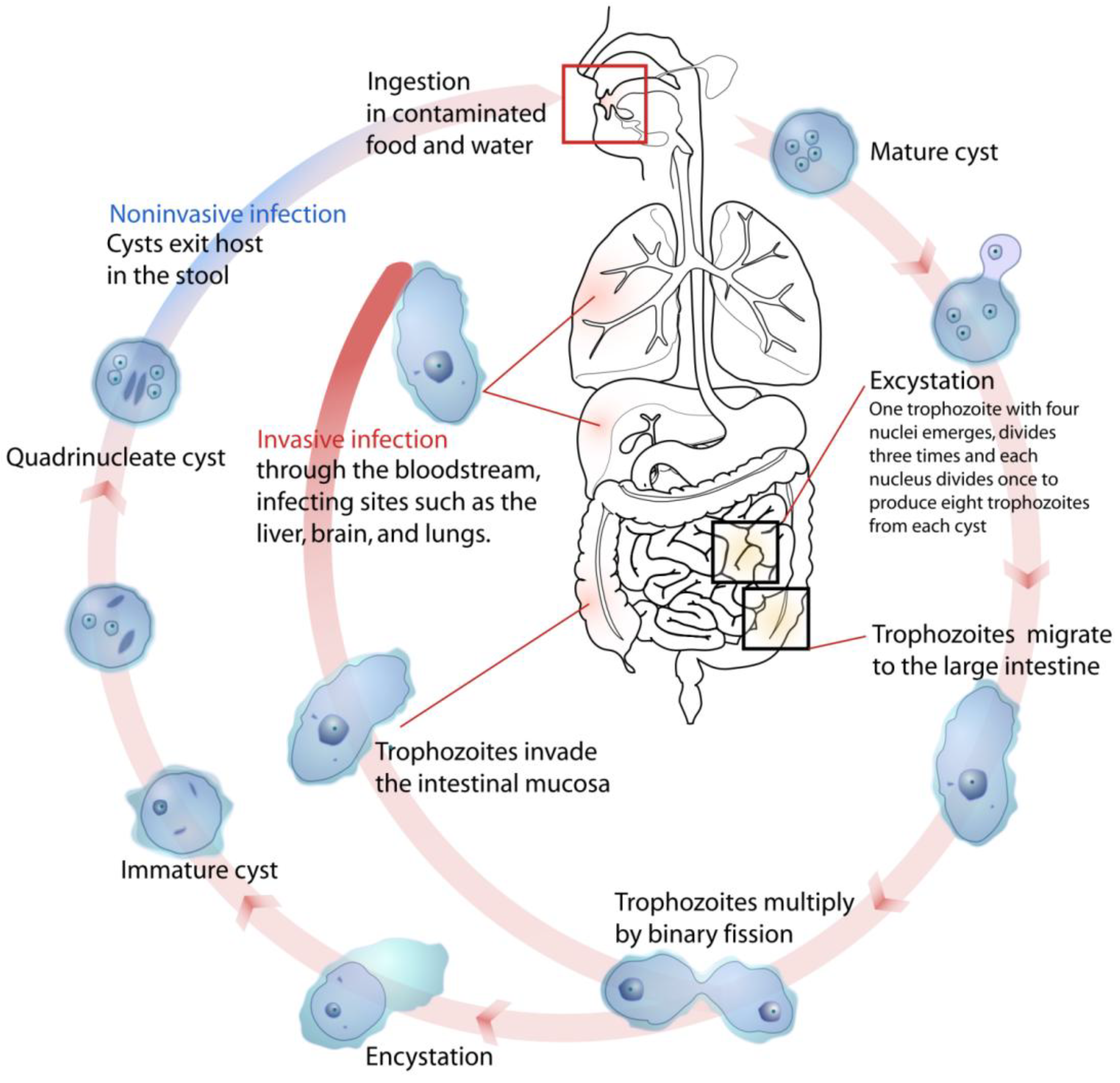
Ijerph Free Full Text Water Related Parasitic Diseases In China Html

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Allergic Proctocolitis Abstract Europe Pmc

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Allergic Proctocolitis Abstract Europe Pmc

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome
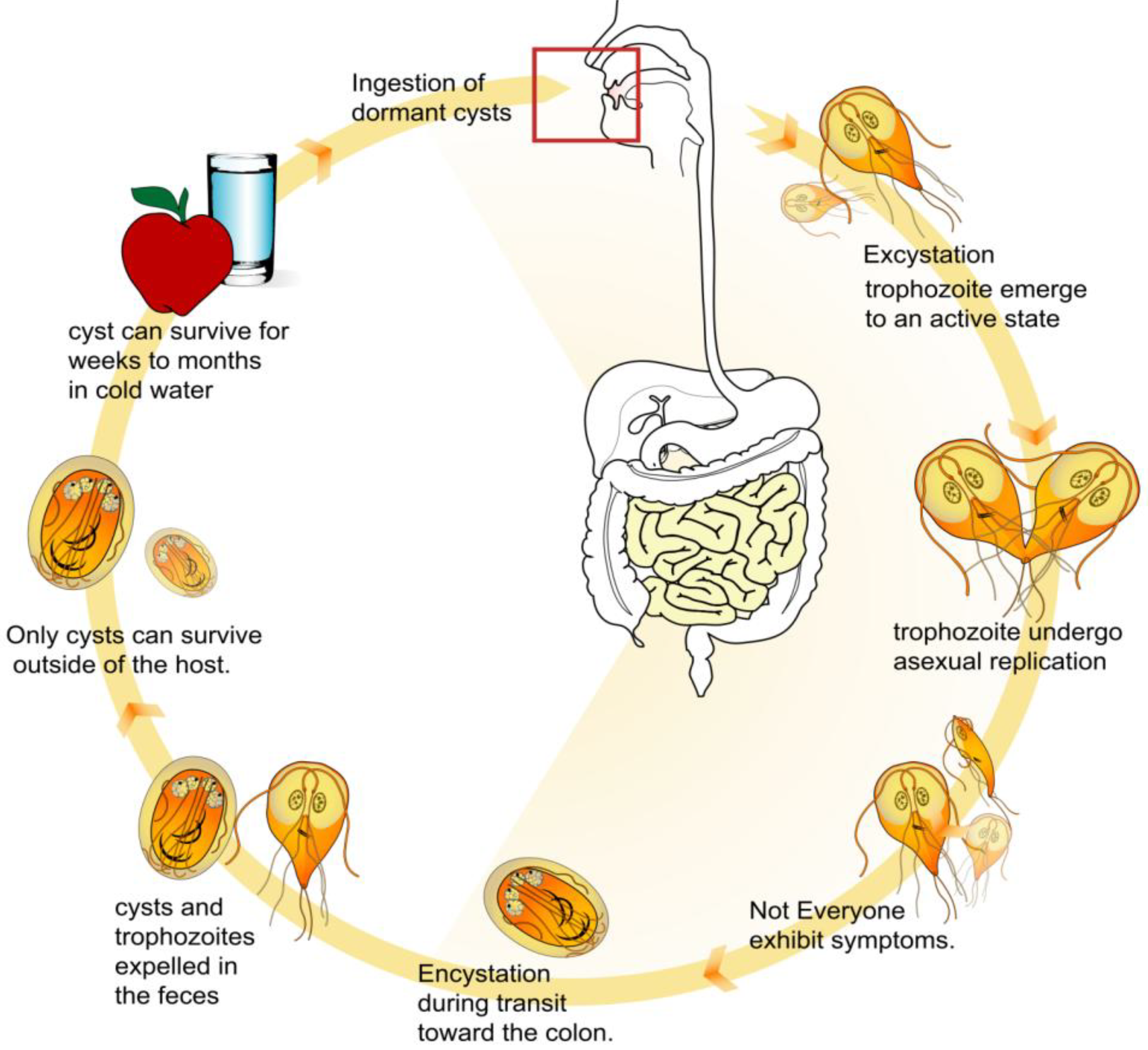
Ijerph Free Full Text Water Related Parasitic Diseases In China Html

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome